About Aquaferrox®
- Enables the sustained immobilization of dissolved heavy metal and metalloid ions/complexes in groundwater by adsorption.
- Enables a long-lasting immobilization effect due to the high adsorption capacity and thermodynamic stability of the goethite particles,
- Is ecotoxicologically safe.
- Can be injected with standard direct-push systems.
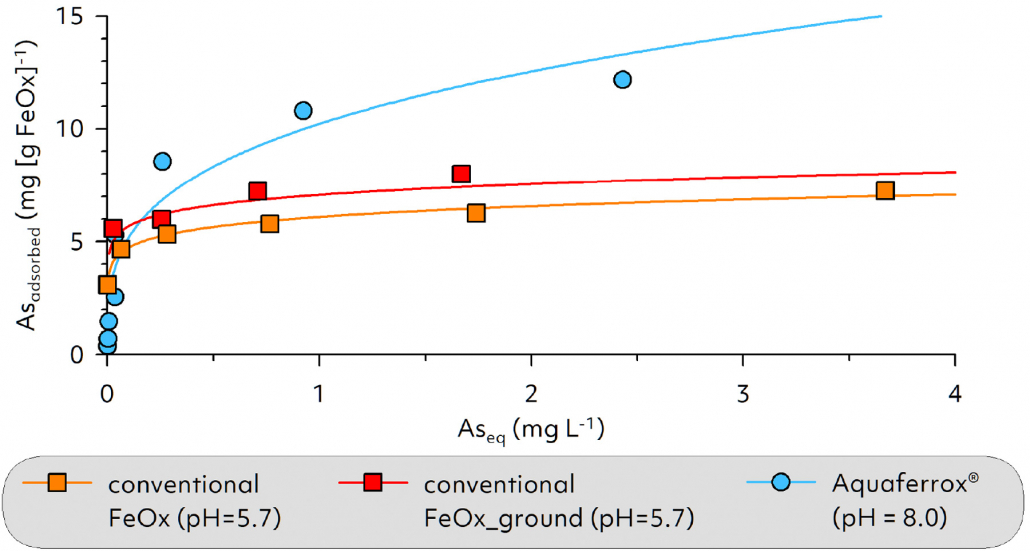
Iron oxides are naturally occurring minerals that form in soils and sediments from the weathering products of Fe-bearing minerals. They have a high specific surface area and a characteristic red/orange color. Iron oxides act as key reactive components in soils and are also responsible for the typical brown coloration of our soils. In industry, iron oxides are used in particular as pigments and as adsorber materials for the immobilization of contaminants.
Aquaferrox® consists of specially prepared goethite particles which – stabilized in colloidal form – are injected into the subsoil. After controlled dispersion, they are immobilized on the aquifer matrix, thus forming an in situ adsorption barrier through which groundwater flows. Due to the high affinity of Aquaferrox® for heavy metals and semi-metals (e.g. As), these contaminants can be immobilized on site without resorting to energy- and cost-intensive measures such as pump-and-treat, excavation or soil washing.